Sara Sentí, Eduard A. van Bodegraven, Alain Sauvanet, Mohammed Abu Hilal, Marc G. Besselink, Safi Dokmak
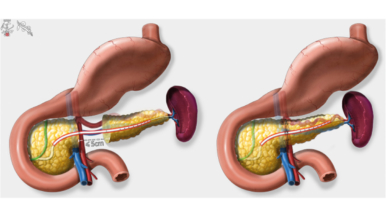
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to give an overview on the postoperative outcome after a minimally invasive (ie, laparoscopic and robot-assisted) central pancreatectomy and open central pancreatectomy with a specific emphasis on the postoperative pancreatic fistula. For benign and low-grade malignant lesions in the pancreatic neck and body, central pancreatectomy may be an alternative to distal pancreatectomy. Exocrine and endocrine insufficiency occur less often after central pancreatectomy, but the rate of postoperative pancreatic fistula is higher.
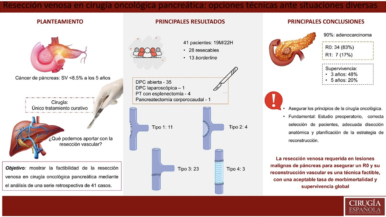
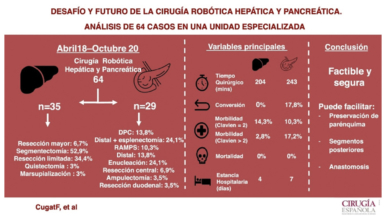
Overall, 41 studies were included involving 1,004 patients, consisting of 158 laparoscopic minimally invasive central pancreatectomies, 80 robot-assisted minimally invasive central pancreatectomies, and 766 open central pancreatectomies. The overall rate of postoperative pancreatic fistula was 14%, major morbidity 14%, and 30-day mortality 1%. The rates of postoperative pancreatic fistula (17% vs 24%, P = .194), major morbidity (17% vs 14%, P = .672), and new-onset diabetes (3% vs 6%, P = .353) did not differ significantly between minimally invasive central pancreatectomy and open central pancreatectomy, respectively. Minimally invasive central pancreatectomy was associated with significantly fewer blood transfusions, less exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, and fewer readmissions compared with open central pancreatectomy.